Sodium Metabisulfite
Also known as E223, Na2S2O5 or SMS
What is Sodium Metabisulfite?
Sodium metabisulfite, or simply SMS, is a reducing agent commonly added to cracker and tortilla doughs that use stronger wheat flours. SMS is also used as a preservative for baked goods, wine, dried fruit, and jams due to its antioxidant capacity.
Origin
Sodium metabisulfite can be made from the reaction between sulfur dioxide with sodium carbonate. The following is the reaction equation:
SO2 + Na2SO3 → Na2S2O5
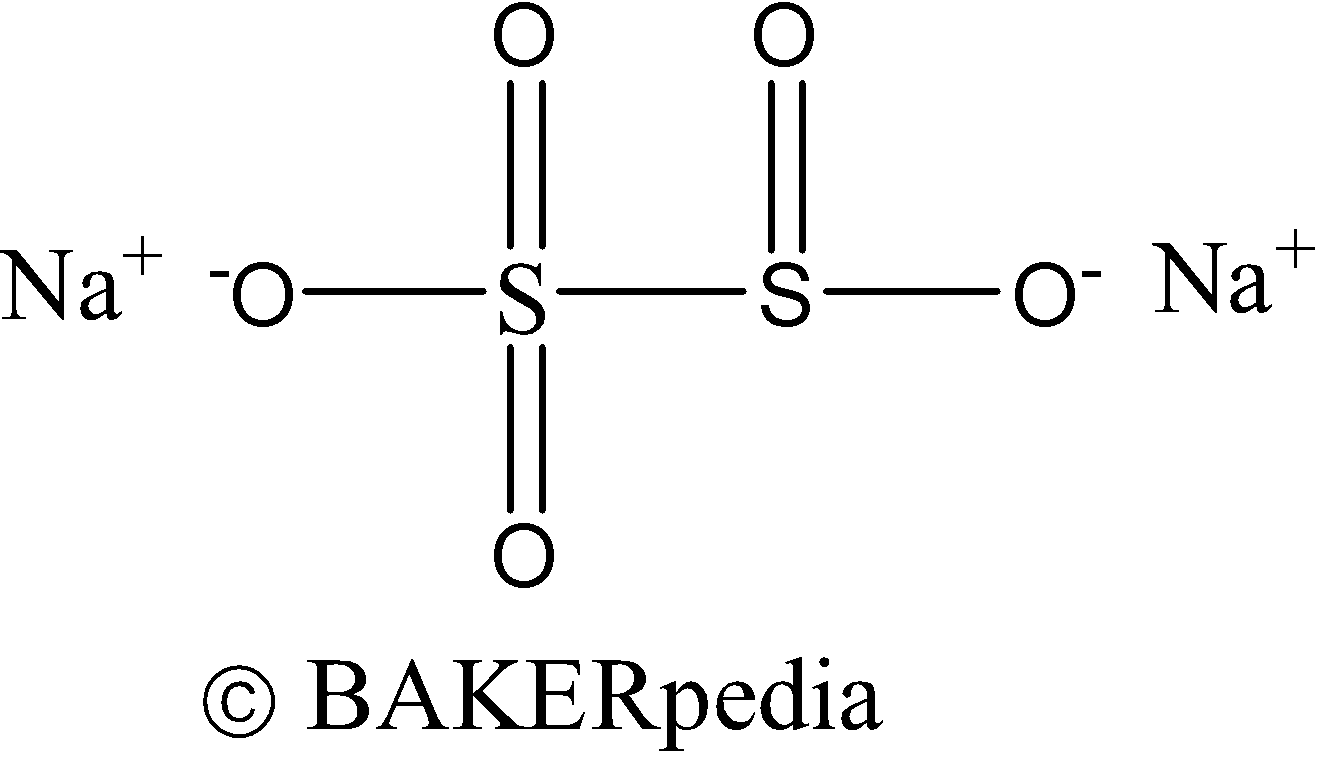
Function
Sodium metabisulfite is an inorganic compound and a versatile bakery ingredient that occurs as crystals or powder having a sulfur dioxide odor. It is readily soluble in water and may perform the following functions in food:
- Antimicrobial agent
- Wheat flour reducing agent
- Antioxidant
Commercial production
Sodium metabisulfite can be produced by crystallizing a solution of sodium bisulfite. Sodium bisulfite results from introducing sulfur dioxide into a solution of sodium sulfite. Sodium sulfite, in turn, can be produced by introducing sulfur dioxide into sodium hydroxide.1
Application
Similar to proteolytic enzymes, sodium metabisulfite is used primarily in the cracker industry to develop a soft and extensible dough with enhanced machinability during sheeting and rolling. SMS is also used for reducing mixing time requirements of strong flours.
Most cracker formulations contain sodium metabisulphite (SMS). It is used in the range of 0.006 to 0.08%, typically at 0.040% (400 ppm based on flour weight. Amounts greater than 800 ppm may cause serious problems with the flour protein quality of the dough. Some sweet baked goods recipes use proteinase, sometimes in combination with SMS.
When used at higher levels, it functions as a preservative to prevent discoloration and bacterial growth. Some consumers may experience adverse reactions to SMS similar to allergy symptoms.
Chemistry behind SMS reducing effect
Unlike L-cysteine or glutathione, sodium metabisulfite does not perform as a reducing agent through sulfhydryl-disulfide interchange. Instead, it reacts with the cysteine amino acids present in glutenins and gliadins, creating S-sulfocysteine residues within the protein structure, which inhibit the formation and/or restoration of disulfide bonds during mixing and rest periods. Essentially, sodium metabisulfite acts as a cap, covering the reactive thiol groups on cysteine residues, so it is unavailable to reform disulfide bonds.2
Regulation
SMS has been confirmed by the U.S. FDA as GRAS when used in accordance with GMPs.3
In the EU, sodium metabisulfite (E223) is listed by the Commission Regulation, EU 231/2012, as an authorized food additive.4
References
- Zolotoochin, V.M., et al. “Patent US5976485 – Sodium Metabisulfite Process.” Google Patents, Google, 2 Nov. 1999, www.google.com/patents/US5976485. Accessed 8 Sept. 2017.
- Fort, E.L. “Effect of Reducing Agents on Batter Consistency and Physical Characteristics of Bread from Sorghum Flour.” Kansas State University Master Thesis, 2016, pp. 25–26.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration, CFR – Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 PART 182 — SUBSTANCES GENERALLY RECOGNIZED AS SAFE, https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=182.3766, Accessed 8 January 2022.
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 1129/2011 of 11 November 2011 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council by establishing a Union list of food additives, https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02011R1129-20131121


